layout_weight and layout_gravity
Description
In LinearLayout, you can apply the layout_weight and layout_gravity attributes to views
contained within it:
Example
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:layout_width="160dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:layout_weight="1" />
<Button
android:layout_width="160dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="2" />
<Button
android:layout_width="160dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:layout_weight="3" />
</LinearLayout>
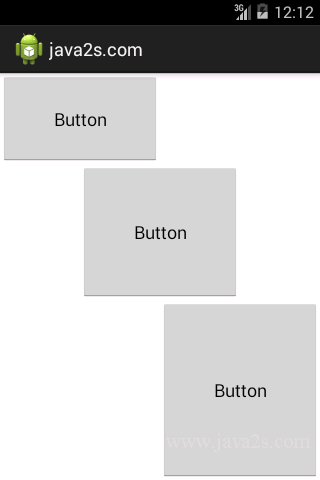
Note
The layout_gravity attribute indicates the positions
the views should gravitate towards.
The layout_weight attribute specifies the distribution of available space.
In the preceding example, the three buttons occupy about
- 16.6% (1/(1+2+3) * 100),
- 33.3% (2/(1+2+3) * 100), and
- 50% (3/(1+2+3) *100)
of the available height, respectively.